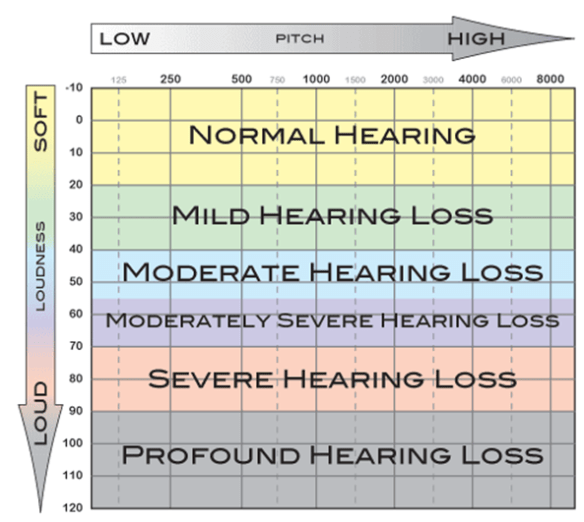
The National Dissemination Center for Children with Disabilities (NICHCY) explains that hearing loss falls into four subcategories: conductive, sensorineural, mixed and central. These identify the location in the body in which the hearing impairment occurs. Hearing aids and other sound amplifying assistive technologies (AT) often work for students with conductive hearing loss, as their impairments stem from the outer or middle ear. Such does not hold true with sensorineural, mixed and central hearing losses, as these impairments stem from the inner ear, the central nervous system or a combination of the two. Typically, hearing loss is categorized as slight, mild, moderate, severe or profound, depending on how well an individual can hear the frequencies that are commonly associated with speech.
Educational Challenges
Educational obstacles related to hearing impairments stem around communication. A student with a hearing impairment may experience difficulty in:
- the subjects of grammar, spelling and vocabulary
- taking notes while listening to lectures
- participating in classroom discussions
- watching educational videos
- presenting oral reports
Underscoring the difficulty that students with hearing impairments may have in presenting oral reports are the potential language development problems linked to hearing impairments. Arizona’s Department of Education’s Parent Information Network notes that, “Since children with hearing impairments are unable to receive some sounds accurately, they often cannot articulate words clearly.”
Hearing Impairment Topic Categories via-
The National Association of Special Education Teachers (NASET)
Hearing Loss in Children Links via ASHA
Audiologic Treatment/Habilitation
Causes of Hearing Loss in Children
Hearing Assistive Technology for Children
Types of Tests Used to Evaluate Hearing in Children and Adults
Resources
Accessibility Considerations Worksheet For Students with Hearing Loss
Causes of Hearing Loss in Children
How to Read an Audiogram and Determine Degrees of Hearing Loss
Students with Hearing Impairment in the School Setting ASHA Practice Policy documents
The Los Angeles Unified School District’s Position Paper Deaf and Hard of Hearing Services
GUIDE TO EDUCATION OF CHILDREN WHO ARE DEAF OR HARD OF HEARING
Sonoma County’s DHH procedures for deaf and hard of hearing (ZIP file with forms)
Assistive Technology in the Classroom For Deaf and Hard of Hearing
Assistive Technologies for Individuals Who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing (from Gallaudet University)

